Adult 7: Men are from Mars, Women are from Venus
- Kamel Marzouki

- Jun 2, 2023
- 25 min read
Men are from Mars, Women are from Venus

The nervous system is responsible for the coordination of a number of processes from crying to the contraction of muscles. The brain lies at the very center of your nervous system with its billions or so of specialized cells known as neurons.
Each of us is born with a brain that some refer to as a hindbrain or reptilian brain. This part of the brain is concerned with your basic life functions such as breathing, digestion, heart rate and other bodily functions. As you grow, your brain grows as well, which is the premise behind the idea that the brain is additive.
The reptilian brain is thought to be the oldest part of the brain and the part of the brain that is concerned with instinct and survival. If you look at the theory of evolution, you would see that humans tended to inherit brain structures from earlier animals and in a sense added on.
Each of us really has three brains:
The reptilian.
The limbic.
The neo-cortex.
Each of these areas works together to help you live your life in a healthy manner. You might also think of these three brains as the reptile brain, the mammal brain, and the human brain. In a sense, the mammal brain looks at survival in terms of social bonding. The reptile brain looks at survival by reacting to threats. The human brain seeks survival by learning from experience.
Every experience in your life adds to your body of knowledge. During those first few years of life, your mammalian brain is the most active, since it deals with the limbic system helping you develop your emotions, connections, feelings and bodings with your friends and family. Your brain is like an onion, in the fact that each new experience adds another complex and unique layer in your life.
All of those experiences in your early years help you form memories - but they're all in the unconscious emotional brain - especially the amygdala, the emotional centers, the emotional memory or the high importance memory parts of the brain.
All of these things at this unconscious or emotional level begin to form your conscious constructs about reality in life.

This model is based on your personal childhood experiences as you build a model of reality in your frontal lobes. Whatever kinds of experiences you have, whether it was a loving mother or an emotionally explosive mother, form your reality throughout life.
After the age of about three, when your conscious central identity is more fully formed, you start to understand this model a little more to the point that you try and predict the future. Your sense of self begins to form and you then start choosing your own identity and, in turn, developing ideas as to how to act in order to get the responses you desire from other people.
This process causes each of us to become more self-aware, which in turn causes us to change our emotions or suppress our emotions in order to fit in. If we experience feelings we don't like, we close them off. On the other hand, if we get the desired result we like, we add these onto our kit of parts.
All of our experiences in our childhood and in our life affect our relationships and intimacy in the future, believe it or not.
We continue changing and modifying until we get where we want to go, and this forms the basis for behavior in our adult life. After a while, it becomes normal for us to suppress, modify and deny or repress our feelings. Every year older we get, we continue to add onto these new beliefs.
With every new experience and trial and error, we add more suppression, more control, more compensation, more reactions and more stuff.

In one sense, we become much more sophisticated and complex. However, at the same time, we create a massive tangle of emotions and beliefs, which cloud our judgment and our perception of reality. This is one of the reasons why people and relationships are so complicated!
Short Term Versus Long Term Memory
Information flows from the outside world into your brain via the senses from things like sight, smell, hearing, tasting and touching. Your memory is the way you store and recall things.
The brain stores sensory information for a fraction of a second in various areas throughout the cortex. After that brief point, the memories then flow into the short-term memory. If the memory is worth saving, it then proceeds into the long-term memory storage.
The short-term memory is very small - and information is typically only stored here for about half a minute, which isn’t very long! The short-term memory can only hold about seven independent items at a time.
Information that may help you in the future is transferred to the long-term memory, where is can last a lifetime. This is often why you might remember all the words to a song you haven't heard in ten years, because thanks to your long-term memory, you can easily retrieve the information if you need it.
Long-term memory is broken down into three processes:
We often break new concepts into separate composites to establish meaning. We might also include some sort of context around that meaning. For example, you might encode something like a crispy red apple to a few key ideas such as the sweet taste, the crisp of the bite and the round shape. You might also put the apple in context by associating it with a cool fall day or a happy experience in your childhood eating apples.
As you store the memory, you then attach it to other related memories. To retrieve memories, your brain establishes various codes in order to decode exactly what you mean or what you are looking for.
The hippocampus, the ancient part of the cortex, is used to consolidate new memories. An event creates a series of temporary links amongst various neurons. For example, "the color red" may get stored in the visual area of the cortex, where the sound of the apple being bitten may get stored in the auditory area.
We are entering a whole new era in neuroscience where technological development allows us to get a full anatomical high-resolution image or rendering of an entire brain circuit.
This ability to “map” and assemble the different anatomical, molecular and functional maps has the potential to advance our understanding of what we know about the brain.
Your brain performs an amazing number of tasks from controlling your blood pressure, to handling physical motion like walking or sitting. In essence, your brain is always analyzing the flood of information from the world around you. Your brain also helps you think, dream and reason and experience complex emotions.
The incredible thing about the brain is that an organ no bigger than a small head of cauliflower does all of these amazing things.
Your brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves comprise a very complex and integrated information processing control system. The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells called neurons and neurons basically transmit electrochemical signals sort of like gates or wires in a computer. Neurons transmit these signals a very long way passing messages to each other.

Within the neuron, there are three basic parts:
The cell body.
The axon.
The dendrites or nerve endings.
The cell body has all the necessary components like the nucleus and mitochondria. The axons are long projections that carry the electrochemical message and the dendrites are small projections that look like branches allowing the neurons to talk with other cells.
The brain is comprised of the brainstem, the cerebellum, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland and the cerebrum or cerebral cortex. The lower brain consists of the spinal cord, the brainstem and something called the diencephalon.
The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain and it contains all the centers that receive and interpret sensory information. This higher part of the brain also initiates movement, analyzes information and is involved in reasoning and experiencing emotions.
The midbrain is actually the smallest part of the brain and it acts as a kind of relay station for both visual and auditory information. The brain is actually hard-wired with connections kind of like a building has electrical wires and cabling.
The cortex pretty much dominates most of the surface of the brain and it is divided into various lobes called the frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobe.

The reptilian brain is said to be the oldest part of the brain. Mammals also have a similar structure and this part of our brain is concerned with instinct and survival.
Electrical synapses transfer information between cells by something called direct ionic coupling. These electrical synapses are both symmetrical and bidirectional, which basically means they can move in two directions. The electrical synapses, or gaps between the brain’s neurons, facilitate information transfer, which is the basis of your thinking and behavior.
Synapses are really just functional units of the nervous system, kind of like switches. In essence, an electrical synapse is really just a mechanical and electrically conductive link between two abutting neurons that is essentially formed at that very narrow gap between something known as a pre and postsynaptic neurons. These gaps are known as gap junctions.
The largest part of the human brain is the cerebrum. The cerebrum is divided into two distinct hemispheres. The brainstem sits underneath the cerebrum and the cerebellum sits behind it.
The cerebral cortex is enlarged in human brains and it is considered the “seat of complex thought.” The brain’s frontal lobes are thought to be associated with higher-level functions like planning, logic, self-control and abstract thought. The occipital lobe handles visual processing and the temporal lobe takes care of sound and language. The temporal lobe, which also includes the hippocampus and amygdala, plays a crucial role when it comes to memory and emotion. The parietal lobe is involved with the different senses and it very important in terms of spatial orientation and navigation.
The brainstem relays information between the brain and body and it also supplies some of the cranial nerves to the face and the head. The brainstem also performs critical functions like controlling the heart, consciousness and breathing.
The left-brain controls things like speech and language and mathematical calculations and fact retrieval. The right brain, on the other hand, is involved with things like visual and auditory processing, artistic ability and special skills, although these types of functions do involve both hemispheres.
Male versus Female Brain
Is there really a big difference between the male and female brain you might ask? According to evolutionary psychology, there is. Research in evolutionary psychology and other related fields tells us that male and female mind's operate distinctly different.
Simon Baron-Cohen of the University of Cambridge, Bernard Crespi of Simon Fraser University, and Christopher Badcock, have all made great contributions in terms of the differences between the male brain and the female brain (Psychology Today, 2008).
The Male Brain
The male brain is characterized by:
Systemizing tendencies- a Baron-Cohen term.
Mechanistic thinking - a Crespi and Badcock term.
Systemizing is that drive to analyze, explore, and construct a system.
The systemizer naturally and intuitively figures out how things work, or he extracts the underlying rules that govern the behavior of a particular system. The underlying purpose of this is to understand and predict the system or to simply invent a new one.
The Female Brain
In contrast, the female brain is characterized by:
Empathizing tendencies - a Baron-Cohen term.
Mentalistic thinking - a Crespi and Badcock term.
Empathizing is that drive to identify another person’s emotions and thoughts, and to respond to them with an appropriate emotion.
Empathizing occurs when we one feels an appropriate emotional reaction in response to the other person’s emotions. The main purpose of empathizing is to understand another person, to predict his or her behavior, or to connect or resonate with him or her emotionally.
As we can see, the main difference overall in the male and female brain is the idea that the male brain is geared more towards analyzing, exploring, and constructing a system whereas the female brain is geared more towards empathizing and responding to various emotions, thoughts and feelings.
In other words, mechanism or the make brain is more about figuring things out where mentalism or the female brain is more about understanding people.
There are many individual exceptions to any generalization, so it's important to keep in mind that every theory or rule has exceptions. In other words, there will always be women who are more geared towards systemizing and men who might be more empathizing.
For example, there will always be some women who are taller than the average man and some men who are shorter than the average woman. However, the overall generalization that men on average are taller than women is still an accurate one.
On the same note, not all men have a strong male brain, and not all women have a strong female brain, but there are still differences between the two. The point is that far more men are more likely to have the male brain and far more women are likely to have the female brain.
These differences between the sexes emerged over time and during the course of human evolution because men and women often faced different pressures.
Psychologists believe that men came to acquire systemizing and mechanical skills because these skills were necessary when it came to inventing and creating tools and weapons.
On the other hand, women developed the ability to empathize because it was needed to facilitate the various aspects of the role of mothering and understanding the needs of infants.
Psychologists also believe that a low empathizing ability was helpful for men in terms of their ability to tolerate solitude during long hunting and tracking trips. This same lack of empathy might have also been helpful for committing acts of interpersonal violence and aggression necessary for male competition.
Women, on the other hand, were tasked with making friends and allies in a changing environment, in which ancestral women found themselves when they married.

According to the late William D. Hamilton, an Oxford evolutionary biologist who was universally regarded as the best Darwinian since Darwin:
“People divide roughly, it seems to me, into two kinds, or rather a continuum is stretched between two extremes. There are people people, and things people,” (Psychology Today, 2008).
According to this particular research, to a large extent, people people are women and things people are men.
Men tend to have a greater ability to systemize and mechanistic skills are the primary reasons why they may be better than women at mathematics, physics, and engineering. All of these fields deal with the various rational systems governed by those particular rules.
Since women have a greater ability to empathize, their mentalistic skills are the primary reason why they may be better at languages and why they may be better judges of character.
Women also dominate "primatology," which, like the mothering of infants, requires a greater understanding and reading of the minds of individuals, with whom they cannot communicate by language (Psychology Today, 2008).
These adaptive differences sometimes misfire and manifest themselves in humorous ways, according to researchers.
For example, men’s tendency toward systemizing and mechanistic thinking may mean that they often try to “figure out” their relationships with their partners as if they are logical systems or a carburetor. What they may fail to realize is that relationships, unlike a logical system, are not always rational or logical.
Psychologists also believe that a low empathizing ability was helpful for men in terms of their ability to tolerate solitude during long hunting and tracking trips. This same lack of empathy might have also been helpful for committing acts of interpersonal violence and aggression necessary for male competition.
When dealing with women or other humans, emotions and feelings must be taken into consideration, because emotions and feelings are anything but rational and logical.
On the opposite note, women often talk to their cars and copy machines, as if they really had feelings, which they don't.
Overall, these sex differences are adaptive. Men and women may actually be different because their brains function in different ways and, as a result, they have much different strengths and weaknesses.
Biological Differences Between the Male and Female Brain
"The science of sex differences has always been – and still is – fraught with controversy. Some believe that behavioural differences between men and women are mostly due to cultural influences, while others argue that sex differences are largely determined by biology. In reality, the situation is far more complex. It lies somewhere in the middle, and involves two related but independent factors, which are often confused or conflated," (The Guardian, 2013).
There have been a lot of controversies when it comes to the differences between men and women. One of these factors lies in the chromosomes.

Most of us have either two X chromosomes, which make us female, or one X and one Y chromosome, which make us male.
The other factor involved is the idea of gender, which tends to be influenced by the process of socialization.
As we grow up and venture out into the world, society tells us or rather shows us how to look and act. There are always people who buck the system of course, but for the most part, we follow the trends of society as it pertains to our gender.
Our gender usually matches these societal norms, but there are exceptions to this rule, and those who happen to be transgender.
Men and women's brains differ in very subtle ways, and these differences are most likely established in the womb thanks to hormones, which either make one masculine or feminine.
There is still a lot that science does not know when it comes to understanding the effects of sex hormones on the developing brain, or how those subtle differences are observed between men and women.

Biological Differences
The most obvious difference between the brains of men and women is overall size.
Men's brains on average tend to be 10 to 15% larger than women's brains.
"In one recent study, neuroscientists compared the brains of 42 men and 58 women postmortem, and found that men's weighed an average of 1,378 g (3 lb), compared with 1,248 g (2.75 lb) for women," (The Guardian, 2013).
These differences in size differences have been noted repeatedly, however, they emerge only when the comparison involves a large number of people. Once again, there are always exceptions to every rule, so some women's brains will be larger than the average whereas some men's brains may be smaller. These differences may partly reflect the fact that men tend to be bigger and taller than women.
Men and women's brains also tend to differ as it pertains to the overall composition.
Men's brains tend to have a slightly higher proportion of white matter, where female brains tend to have a higher proportion of gray matter in most parts of the cerebral cortex (The Guardian, 2013).
Consequently, the cortex is slightly thicker in women's brains than in men's and, according to several studies, is slightly more convoluted as well (The Guardian, 2013).
There are also sex differences in the size when it comes to individual brain structures. The hippocampus, which is a structure that is involved in the formation of memories, is on average larger in men than it is in women.
The amygdala, which is also involved in memory and emotions, is also larger in men (The Guardian, 2013).
"Another sexual variation is found in a structure called the third interstitial nucleus of the anterior hypothalamus. The function of this tiny structure is unknown, but research from four different laboratories has repeatedly found that it is almost twice as large in males than in females," (The Guardian, 2013.)
Myths and Stereotypes
Many studies have shown subtle differences between male and female behavior as well as cognitive functions.
"Men tend to be more aggressive and outperform women on mental tasks involving spatial skills such as mental rotation, whereas women tend to be more empathetic and perform better on verbal memory and language tasks," (The Guardian, 2013).
Findings like these may even be exaggerated to reinforce the stereotypes that often plague men and women.
In some cases, individual studies that supposedly show sex differences between men and women are even misappropriated. For example, according to a tiny postmortem study published in 1982, the corpus callosum, which is the massive bundle of nerve fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres, is proportionally larger in women than in men.
This was widely reported to mean that women are better at multitasking, even though future studies have failed to replicate the same results. A more recent study showed that women were marginally better than men when it came to paying attention to sounds presented to both ears simultaneously – and this was interpreted by some as evidence that 'men don't listen'.
"Many of these claims are accompanied by the assertion that the observed differences between men and women's brains are 'hard-wired' and, therefore, irreversible,"(The Guardian, 2013).
Scientists now know that brain structure and function can actually change depending on the upbringing and socialization factors, however, very little research has actually been done to investigate how different nurturing styles might also influence brain development.
The extreme male brain hypothesis
People with autism tend to perform poorly on tests when it comes to empathizing. In other words, on tests that required them to put themselves in someone else's shoes. However, they do well on tests that require them to use the idea of systematizing, or finding repeating patterns.
Women tend to score higher on the empathy scale while men tend to score higher on the systematizing scale.
"These observations led one researcher to propose the highly controversial 'extreme male brain' hypothesis of autism. The hypothesis states that autism is an extreme form of the normal male cognitive profile, which occurs as a result of high testosterone levels in the womb," (The Guardian, 2013).
According to the research, those with autism might even be considered as 'hyper-systematizers' or people who focus more on patterns and fine details than on other people's thoughts and actions, which makes sense when you examine the dynamic of autism (The Guardian, 2013).
This extreme viewpoint may even be an explanation as to why autism is four times more prevalent in males than in females. Moreover, it might also explain why people with autism often excel in disciplines such as math and engineering.
Potential Barriers to Relationships

The differences between women and men are well documented. They also make for great fun and are often brought up at parties and used in jokes.
The experts have discovered that there are actually some very big differences in the way women’s and men’s brains are structured and in the way they react to certain stimuli and events.
All of this might come in handy, the next time your wife or your boyfriend starts telling you how you should have done something differently.
Ten Big Differences Between Men's and Women's Brains
1. The way they handle relationships.
Women, for the most part, tend to communicate much more effectively than their male counterparts. Women tend to focus more on how to create solutions that work for the group, often talking through issues, and utilizing non-verbal cues such as tone, emotion, and empathy. Men, on the other hand, tend to be a little more task-oriented, and less talkative, and, even more, isolated.
Men may also have a more difficult time understanding certain emotions, especially emotions that are not explicitly verbalized. Women, tend to be more intuitive, sensing emotions and emotional cues. These differences might explain why men and women sometimes have a whole lot of difficulty communicating and why men-to-men friendships look a little different from friendships amongst women.
2. Left brain vs. both hemispheres.
Overall, men tend to process better in the left hemisphere of the brain while women may actually process equally well between both the left and right hemispheres.
This subtle difference might also explain why men are generally stronger when it comes to left-brain activities, often approaching problem solving from a task-oriented perspective with women typically solving problems more creatively.
Women are also more aware of their feelings while communicating.
3. Mathematical abilities.
There is an area of the brain known as the inferior-parietal lobule (IPL) and it is typically significantly larger in men, especially on the left side than in women (Masters of Healthcare, 2009).
This section of the brain is also thought to control mental mathematical abilities, and it probably explains why men frequently perform higher in mathematical tasks than women.
The inferior-parietal lobule (IPL) is the same area of Einstein’s brain that was discovered to be abnormally large.
"The IPL also processes sensory information, and the larger right side in women allows them to focus on, "specific stimuli, such as a baby crying in the night," (Masters of Healthcare, 2009).
4. Reaction to stress.
Men tend to utilize the "fight or flight" response when it comes to stressful situations while women seem to approach this same kind of situation with a "tend and befriend" strategy.
"Psychologist Shelley E. Taylor coined the phrase 'tend and befriend' after recognizing that during times of stress women take care of themselves and their children (tending) and form strong group bonds (befriending)," (Masters of Healthcare, 2009).
The reason for these subtle reactions to stress may be rooted in hormones. The hormone known as oxytocin is actually released during stressful events in everyone. However, the hormone estrogen tends to enhance oxytocin, resulting in a calming and nurturing feeling. Testosterone, on the other hand, which men produce in high levels during stress, serves to reduce the effects of oxytocin.
5. Language.
Two sections of the brain responsible for language were found to be larger in women than in men, which might be one reason why women typically excel in language-based subjects and in language-associated thinking.
Research also tells us that men typically only process language in their dominant hemisphere, whereas women actually process language in both hemispheres.
This difference may also be the reason that women may be able to recover more fully from strokes that affect the language areas in the brain while men may not have this same advantage.
6. Emotions.
Women typically have a larger deep limbic system than men, which might allow them to be more in touch with their emotions and feelings, enabling them to better express them.
This tendency also promotes bonding with others. Because of this unique ability to connect, more women serve as caregivers for children
The downside to this larger deep limbic system is that it may also open women up to more occurrences of depression, especially during those times of hormonal shifts such as after childbirth or during a woman’s menstrual cycle.
7. Brain size.
Typically, men’s brains are 11-12% bigger than women’s and this size difference has nothing to do with intelligence. Men also need more neurons to control their greater muscle mass and their larger body size, thus, they generally have a larger brain.
8. Pain
Men and women definitely perceive pain differently. In research studies, it was shown that women require more morphine than men to reach the same level of pain reduction. Women are also more likely to vocalize their pain and to seek treatment for their pain when compared to men.
"The area of the brain that is activated during pain is the amygdala, and researchers have discovered that in men, the right amygdala is activated and in women, the left amygdala is activated," (Masters of Healthcare, 2009).
9. Spatial ability.
Men typically have a stronger sense when it comes to spatial abilities, or being able to mentally represent a shape and its dynamics. Women, on the other hand, tend to struggle more in this area. Medical experts have also discovered that women have a thicker parietal region of the brain, which hinders their ability to mentally rotate objects–an aspect of spatial ability.
Research has proven this ability in babies as young as 5 months old, negating any ideas that these abilities were strengthened by environmental influences.
10. Susceptibility to disorders.
Because of the way men and women use the two brain hemispheres differently, there are some disorders that affect men and women differently.
Information complements of Masters of Healthcare, 2009.
Men are much more apt to have dyslexia or other kinds of language problems when compared to women.

Women with dyslexia are also much more likely to compensate for it. On the other side of the coin, women are also much more susceptible to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
These brain tendencies also might explain why more men are left-handed than women and why more men are more likely to be diagnosed with autism, ADHD, and Tourette’s Syndrome.
What Do Brain Scans Tell Us?
Typical neural map of a man's brain (Photograph: National Academy of Sciences/PA).
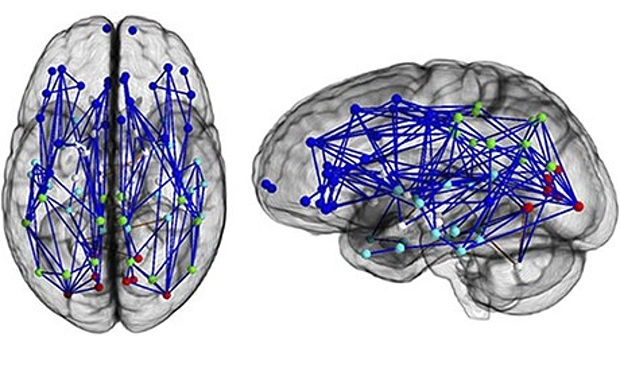
"Scientists have drawn on nearly 1,000 brain scans to confirm what many had surely concluded long ago: that stark differences exist in the wiring of male and female brains (The Guardian, 2013)."
Neural circuitry maps have shown that on average women's brain were more highly connected across the left and right hemispheres. In contrast, men's brains were stronger between those front and back regions.
Ragini Verma, a researcher at the University of Pennsylvania, was surprised that the research supported old stereotypes so much, showing that men's brains were apparently wired more for perception and coordinated actions. Women's brains, on the other hand, were wired more for social skills and memory, making them better equipped for multitasking.
"If you look at functional studies, the left of the brain is more for logical thinking, the right of the brain is for more intuitive thinking. So if there's a task that involves doing both of those things, it would seem that women are hardwired to do those better," (The Guardian, 2013)."
Verma continued by saying:
"Women are better at intuitive thinking. Women are better at remembering things. When you talk, women are more emotionally involved – they will listen more," (The Guardian, 2013)."
The researcher was surprised that brain scans matched a lot of the stereotypes that have been in place for many years.
These neural maps show how the brains of males versus females are wired and they give scientists a much more complete picture of the brains of each sex at different ages. With more research scientists will be able to learn more about whether abnormalities in brain connectivity affect brain disorders such as depression and schizophrenia.
"Verma's team used a technique called diffusion tensor imaging to map neural connections in the brains of 428 males and 521 females aged 8 to 22. The neural connections are much like a road system over which the brain's traffic travels," (The Guardian, 2013)."
These scans showed a greater connectivity between the left and right sides of the brain in women, with the connections in men mostly confined to the individual hemispheres.
The only region where men had more connections between the left and right sides of their brains was in the cerebellum, which plays an integral role in motor control.
"Detailed connectome maps of the brain will not only help us better understand the differences between how men and women think, but it will also give us more insight into the roots of neurological disorders, which are often sex-related," (The Guardian, 2013)."
Relationships and the Brain
People in relationships often have very strong expectations when it comes to their partner. For example, they might think that their partner will be just like they are in terms of their attitudes, their values or their perceptions and behaviors.
However, as most of us already know, you can't really change other people, you can only change yourself!
In other words, you must be the change you want to see.
Most of us already know that it is difficult to change your partner's attitudes and behaviors, unless they are already motivated to do so.
You are even less likely to change attitudes and behaviors based on basic gender characteristics. Because of this, it's important to be aware of what those basic differences are.
The fact is that these gender differences do exist between men and women, so the best plan of action is to arm yourself with knowledge and realize that these differences make your partner who they are.
It's better to use these differences to enrich your relationship, rather than spend your time trying to change them.
Are Men and Women really that different?
Looking at the evidence, we can see that there are some substantial differences when it comes to men versus women.
(Note that these findings are generalizations and summaries only - in other words, they apply to most men or women, but not to all men or all women. (Relationship Institute, 2015).
Psychological Differences

Girls develop the right side of the brain faster than boys do:
This leads to:
Talking
Vocabulary
Pronunciation
Reading earlier
Better memory

Boys develop the left side of the brain faster than girls:
This leads to:
Visual-spatial-logical skills
Perceptual skills
Better at math
Problem-solving
Building and figuring out puzzles
Girls are also more interested in toys that happen to have faces on them and they play with dolls and stuffed animals more. Boys, on the other hand, are more drawn to blocks or anything that can be manipulated.
Women use both hemispheres of the brain, and the corpus callosum is thicker in women.
Social Influences
In studies done with infants:
Both women and men speak louder to boys than they do to girl infants.
Both women and men are softer, expressing more “cooing” with girls.
Boys are rarely told they are pretty or sweet, but instead told they told they are a pumpkin head or “Hey big guy”.
Boys are even handled more physically and more robustly than girls, and they are bounced around more.
Girls are caressed and stroked much more than boys.
Up until the age of two, mothers tend to talk to and even look at their daughters much more than they do with their sons. They also make a lot more eye contact with their daughters as well.
In terms of emotional response, mothers showed a wider range of emotional response to girls than boys. When girls did show anger, their mother's often show disproval which is also a big reason why girls grow up smiling more than boys. Girls also tend to be more social.
Developmental Differences
Books and nursery rhymes and even cartoons typically portray stereotypes such as the damsel in distress, the frumpy housewives, the sexy heroine or the swooning cheerleader.
While girls use more terms of endearment when compared to boys, it is the boys who get away with more aggressive antisocial behavior in school and at home.
Girls who act as tomboys are usually accepted while boys who act like girls are severely reprimanded.
Girls tend to talk about other people and share secrets in order to bond with other girls while boys talk about activities and things.
Teenage girls talk about boys, their weight, and clothing while teenage boys talk about sports, mechanics, and the functions of things.
The biggest event for girls ages 12-18 is having a boyfriend while boys that same age are more interested in sex, cars, and sports.
All of these things and characteristics carry into adulthood so women end up talking about people, relationships, their diet, their appearance and clothing while men talk about sports, work, money, the news, politics and the mechanics of things.
Values and Self-Esteem Going into Adulthood
Characteristics of Men
A man’s sense of self is defined mainly through his ability to achieve results, and through success and accomplishment. Men want to prove their competence and feel good about themselves and they must achieve their goals by themselves.
To do things by themselves is a symbol of great power, efficiency and competence. Men are also more interested in objects and things rather than feelings and people.
Men rarely talk about their problems unless of course they happen to seek advice from an expert.
Men are more aggressive than women, and often more combative and territorial.
Men’s level of self-esteem tends to be more career-related.
Men feel devastated by financial setbacks or failure and they tend to obsess about money much more so than women.
Men hate to ask for information or directions, as we all know because it shows they are a failure.
Characteristics of Women
Women value things like communication, relationships, love, and beauty. A woman's sense of self is often defined via their thoughts and feelings as well as the quality of their relationships.
Women spend much more time supporting, nurturing and helping others and they experience a sense of fulfillment through sharing and relating.
Personal expression is often shown through clothing and feelings and communication.
Women enjoy sharing, relating and talking because this makes them feel good about themselves.
Offering help is not a sign of weakness but a sign of strength for women and a sign of caring to give support.
Women are also very concerned about issues relating to physical attractiveness; and changes in this area can be as very difficult for women - as difficult for men as changes in financial status.
If men are preoccupied with work or money, women interpret this as rejection.
Other Key Differences
Men tend to be more logical, analytical and rational.
Women tend to be more intuitive, holistic, integrative and creative.
Men have a more difficult time when it comes to relating to their own feelings, and they may even feel threatened by the expression of feelings in their presence.
This, in turn, may cause them to react by withdrawing or attempting to control the situation through a display of power or control.
Men are more vulnerable and dependent on relationships than women are and as a result, are often more devastated by a relationship ending, since they have fewer friends and sources of emotional support.
Men are more comfortable with their own angry feelings than women are.
Women tend to be more in touch with a much wider range of feelings when compared to men, and the intensity of those feelings is usually much greater for women.
As a result of this, many men perceive that women’s feelings appear to change quickly and men may find this irrational or difficult to understand.
Men tend to be more functional when problem-solving and women are more aesthetically-oriented in addition to being functional.
Women tend to be much more sensitive to smells and sounds and as a result, they tend to place a greater emphasis on atmosphere.
Conflicts that Can Arise
The most frequent complaint men have about women is that women are always trying to change them! The most frequent complaint women have about men is that men don’t listen!
While men offer solutions, women want empathy. If a woman tries to improve or correct or give advice to a man it is often interpreted as a lack of competence in their skills. Men also feel responsible or to blame for some reason when it comes to women's problems.
Men also might assume that women want advice or solutions to problems, but the truth is they just want someone to listen sincerely.
Men avoid housework at all costs and feel demeaned doing it. Women look at a clean house as a warm, homey nest. Men and women also have many different thresholds when it comes to dirt and cleanliness.
Men often try to change a woman’s mood by offering solutions to her problems when she is upset, which she interprets as discounting or invalidating her feelings.
Women might also try to change men’s behavior by offering unsolicited advice and criticism or becoming a home-improvement committee.
How Can You Work With These Differences?
When women are upset, it is much better to be empathetic and to be a good listener rather than try and offer immediate solutions. It may be more appropriate to offer advice or solutions at a future time when she is calmed down.
On the other side of the spectrum, a man actually appreciates advice and criticism when they request it. Men want to make improvements and they appreciate advice and solutions.
Men have a great need for status and independence while women have more of a need for intimacy and connection.
Women need to receive:
Caring
Understanding
Respect
Devotion
Validation
Reassurance
Women are also much more motivated when they feel special or cherished.
Men need to receive:
Trust
Acceptance
Appreciation
Admiration
Approval
Encouragement
Men are more motivated when they feel needed and a man’s deepest fear is that he is not good enough or not competent enough, although he may never express this.
All in all, there are major and significant differences between men and women and the more you seek to understand these unique differences, the better you will able to handle and effectively communicate with the opposite sex.
The differences are just that - different, they are NOT better or worse. It's best not to judge the differences and or try and make them go away and it's important to remember that you can change the differences.
The best approach is not judging the differences - but respecting them.
To get along with the opposite sex, you MUST expect, accept and respect these differences





